Crossing and Incident Angles
Crossing or Docking Angle (TCR Twist)
The crossing or docking angle is the angle between the MHC pocket (peptide binding groove) and the vector between the TCR domains; the latter is calculated using the centroids of the conserved disulfide bonds in each domain. This corresponds to the twist of the TCR over the peptide-MHC, and its calculation here follows the methodology described by Rudolph, Stanfield, Wilson (Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006).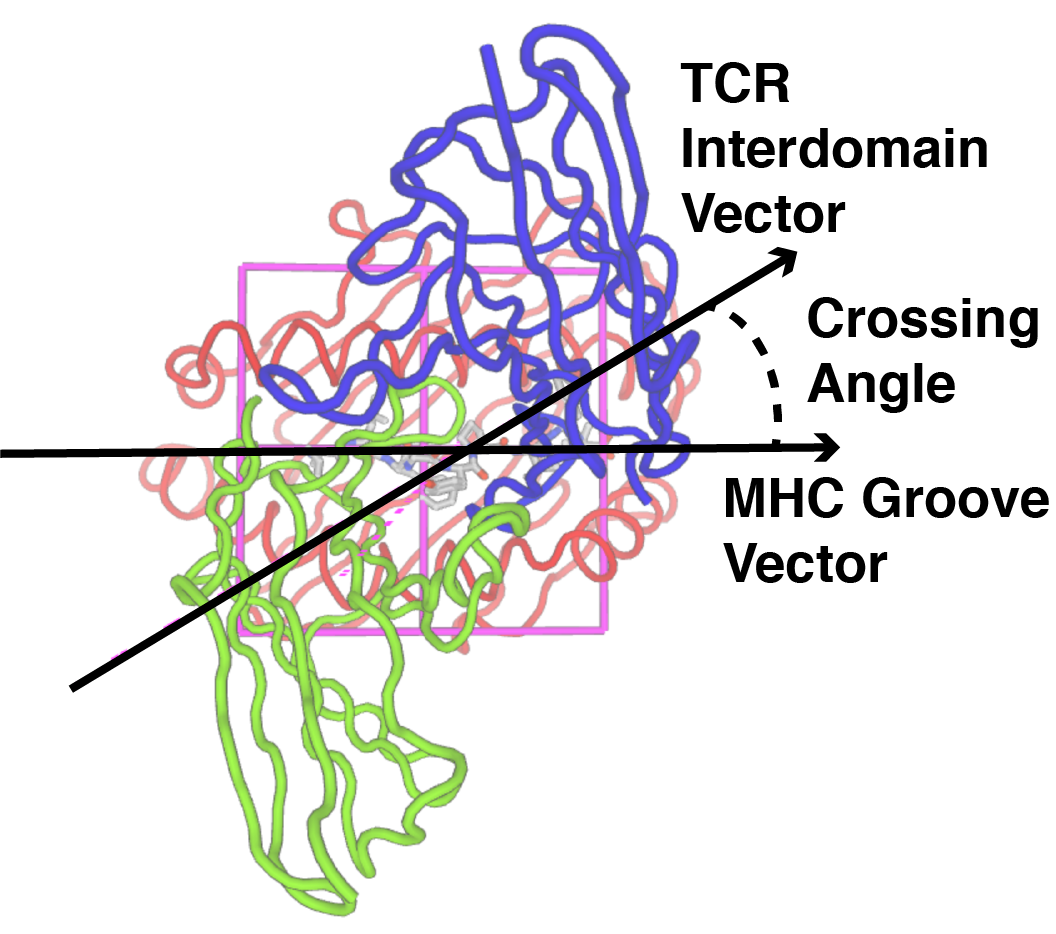
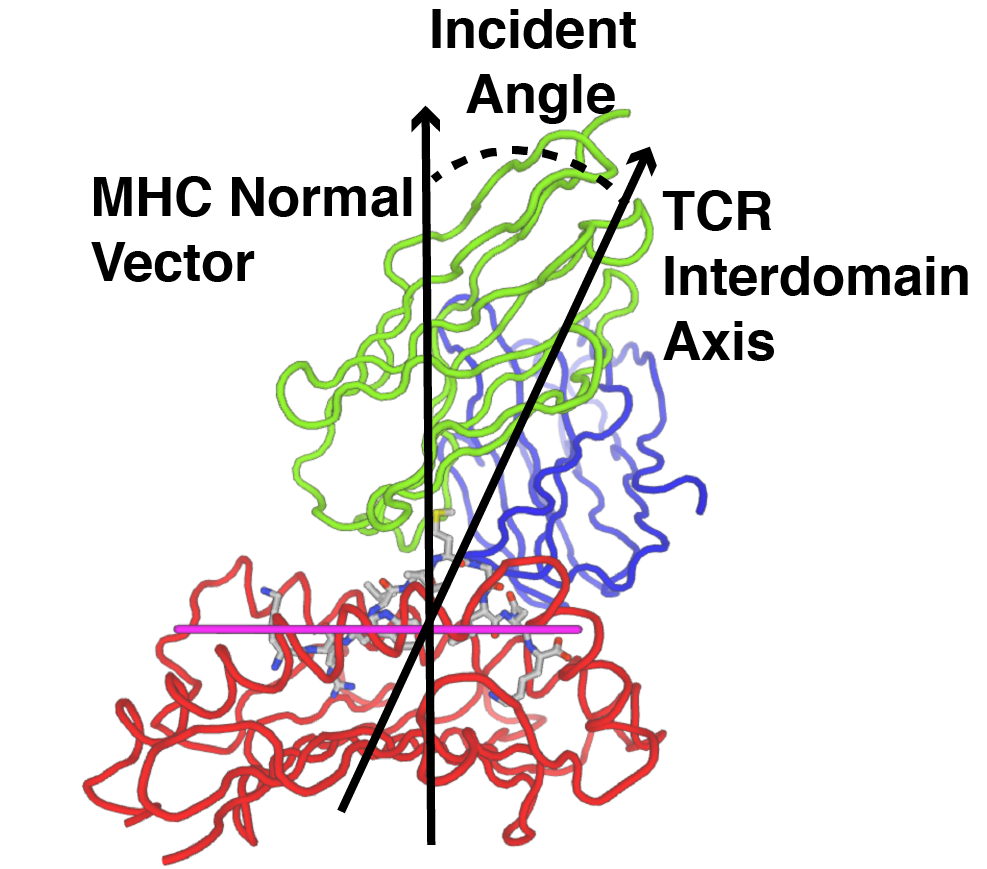
Incident Angle (TCR Tilt)
The incident or tilt angle is the angle between the MHC peptide groove plane normal vector and the TCR interdomain axis of rotation. This corresponds to the degree of tilt of the TCR over the peptide-MHC.